Introduction
In business world, IT infrastructure is the backbone of every organization. From managing devices and software licenses to ensuring service uptime and smooth workflows — it all depends on two crucial frameworks: IT Asset Management (ITAM) and IT Service Management (ITSM).
While these two terms are often used interchangeably, they serve distinct yet complementary roles in maintaining IT efficiency. Understanding ITAM vs ITSM can help organizations eliminate redundancy, improve compliance, and reduce operational costs..
In This Blog, We Will Cover:
- What is ITAM and ITSM?
- The core differences between ITAM vs ITSM
- Best practice for integrating ITAM and ITSM
- When Should You Prioritize ITAM vs ITSM?
- Key KPIs to measure ITAM effectiveness
- Conculsion
What Is ITAM?
ITAM (IT Asset Management) covers the full lifecycle of IT assets—procurement, deployment, usage, maintenance, and disposal. It’s about understanding what you own, how it’s being used, its cost, compliance obligations, and roadmap for renewal or retirement.
For example:
You procure 100 laptops, track serial numbers, monitor warranty status, assign them to users, and eventually retire or sell them.
- ITAM ensures you never lose track, overspend, or violate licensing rules.
What Is ITSM?
ITSM (IT Service Management) focuses on delivering IT as a service to users. It’s about managing incidents, service requests, changes, and ensuring the IT services align with business goals and SLAs (Service Level Agreements).
When a user’s laptop fails or software crashes, the service desk (a core ITSM function) handles the request, escalates it, resolves it, and records metrics. ITSM ensures service reliability, continuity, and user satisfaction.
So: ITAM is about what you have; ITSM is about how you serve.
ITAM vs ITSM: The 7 Key Differences
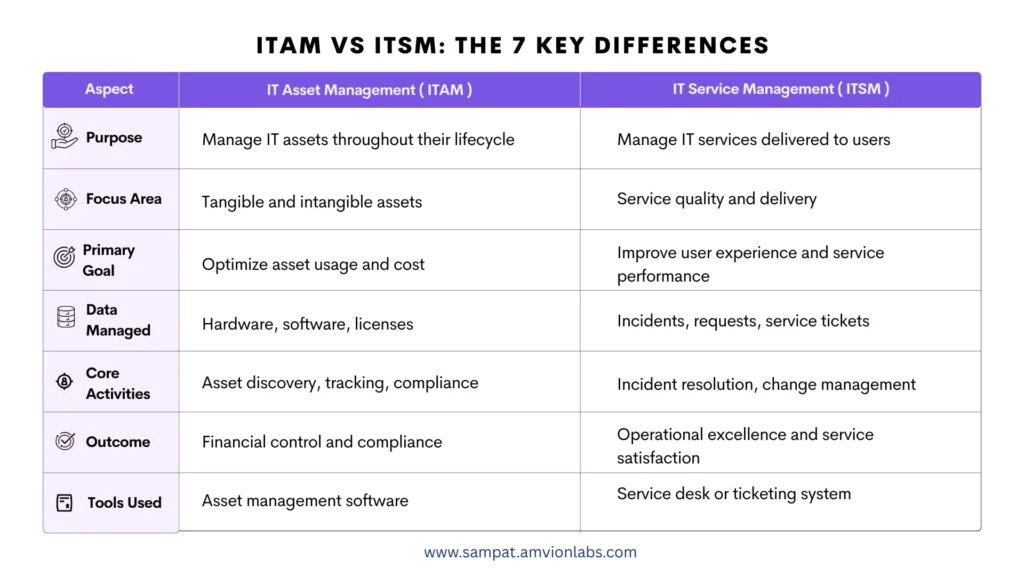
While ITAM is more asset-centric, ITSM is service-centric. Yet, both are essential for creating a resilient, cost-effective IT environment.
Best Practices for Integrating ITAM and ITSM
Bringing ITAM and ITSM together is not just about connecting two tools — it’s about creating a unified operational model. Here are some best practices to achieve seamless integration:
1. Centralize Asset and Service Data
Use a unified platform or ensure integration between ITAM and ITSM tools so both share real-time asset and service information. This eliminates data silos and enables data-driven decisions.
2. Automate Asset Discovery
Manual tracking leads to inaccuracies. Implement automated discovery tools that continuously scan your network and update the asset database whenever new devices or software appear.
3. Align Asset Lifecycle with Service Delivery
Link every asset to its corresponding service. For instance, if a laptop is linked to an employee’s profile, its service tickets, updates, and incidents should also be visible in one view.
4. Implement Governance and Compliance Policies
Ensure your ITAM-ITSM integration follows industry standards like ISO/IEC 19770 for ITAM and ITIL for ITSM. This reduces audit risks and improves accountability.
5. Track Asset Performance Through Service Metrics
Service performance often depends on the health of assets. By monitoring hardware uptime and software usage patterns, you can preempt potential issues before they affect services.
When Should You Prioritize ITAM vs ITSM?
Depending on your organization’s maturity and pain points:
- New or small organizations might start with ITSM, to manage service requests and incidents, then layer ITAM.
- Asset-heavy environments (manufacturing, healthcare) may start with ITAM to gain control over costs and compliance.
- The best path: build both simultaneously so they evolve together, rather than trying to bolt one onto the other later.
Many modern frameworks (ITIL, ISO/IEC 19770) encourage convergence of ITAM and ITSM.
Key KPIs to Measure ITAM Effectiveness
You can’t improve what you don’t measure. Tracking KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) ensures your ITAM strategy is both efficient and cost-effective.
Here are some essential ITAM KPIs to monitor:
1. Asset Utilization Rate
Measures how effectively assets are being used. A high utilization rate indicates optimal usage, while a low rate points to underused or idle assets.
2. License Compliance Rate
Tracks the percentage of software assets that comply with licensing agreements. This helps prevent financial penalties and maintain vendor trust.
3. Asset Lifecycle Cost
Calculates the total cost of ownership (TCO) from purchase to disposal. This metric helps identify cost-saving opportunities and improve procurement decisions.
4. Mean Time to Resolve (MTTR) Asset Incidents
Measures how quickly asset-related incidents are resolved — an excellent KPI for understanding how well ITAM supports ITSM processes.
5. Asset Downtime
Indicates how often assets experience downtime, directly impacting productivity and service levels.
6. ROI from ITAM Initiatives
Evaluates financial benefits achieved through better asset tracking, reduced wastage, and improved lifecycle management.
By monitoring these KPIs, businesses can move from reactive IT asset management to a strategic, proactive approach that drives measurable business value.
Conclusion
Understanding the distinction between ITAM vs ITSM is more than semantics—it’s the foundation for optimizing your IT ecosystem. While ITAM ensures financial, contract, and lifecycle control, ITSM delivers operational excellence and user satisfaction.
🔍 Want to see how a unified system can transform both your asset and service management? Let me know—I’d be happy to walk you through it. Get a demo.
Frequently Asked Question
What is the difference between ITSM and ITAM?
ITSM focuses on delivering and managing IT services, while ITAM manages the lifecycle, cost, and compliance of IT assets.
What are the key components of ITAM vs ITSM?
ITAM includes asset discovery, inventory, licensing, lifecycle, and compliance.
ITSM includes incident, problem, change, service request, and service delivery processes.
Is ITAM part of ITSM or a separate function?
ITAM is often a subset of ITSM but can also function independently depending on the organization.
How do ITAM and ITSM work together in IT operations?
They work together by connecting asset data with service processes, improving troubleshooting, reducing downtime, and enabling informed decision-making.
Do ITAM platforms offer ITSM capabilities?
Some ITAM tools include basic ITSM features, but full ITSM capabilities usually require a dedicated ITSM system.


